01-25-2022: Nanoscribe introduced Quantum X align—a revolutionary 3D micro-printing machine for optical fibers
The system automatically detected optical interfaces and the orientations of photonic chips and fiber cores, enabling the 3D printing of micro optics in any shape
On January 25, 2022, Nanoscribe—a pioneer in Two-Photon Polymerization (2PP) 3D printing technology—announced the launch of its groundbreaking 3D printer, Quantum X align. This high-precision 3D micro-printer enabled the creation of micro-optical elements with any shape, printed directly onto optical fibers and photonic chips. The system made its debut at Photonics West 2022 in San Francisco, USA.
Nanoscribe, founded in 2007 as a spin-off from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), was acquired in June 2021 by BICO Group (formerly CELLINK) in a €35 million deal. By the end of 2024, however, the company changed hands again, being sold to LAB14 GmbH for $26 million. Over the years, Nanoscribe has established itself as a leader in the micro-printing space, serving more than 3,000 customers globally, including universities, research institutions, and industrial companies.
The company’s product portfolio included cutting-edge microsystems such as Quantum X, Quantum X shape, Quantum X bio, and the Photonic Professional GT2. To support applications in microfluidics and micro-optics, Nanoscribe also offered a proprietary range of specialized resins, including the IP Photoresin series for photopolymer parts and GP-Silica material for silica glass microstructures.
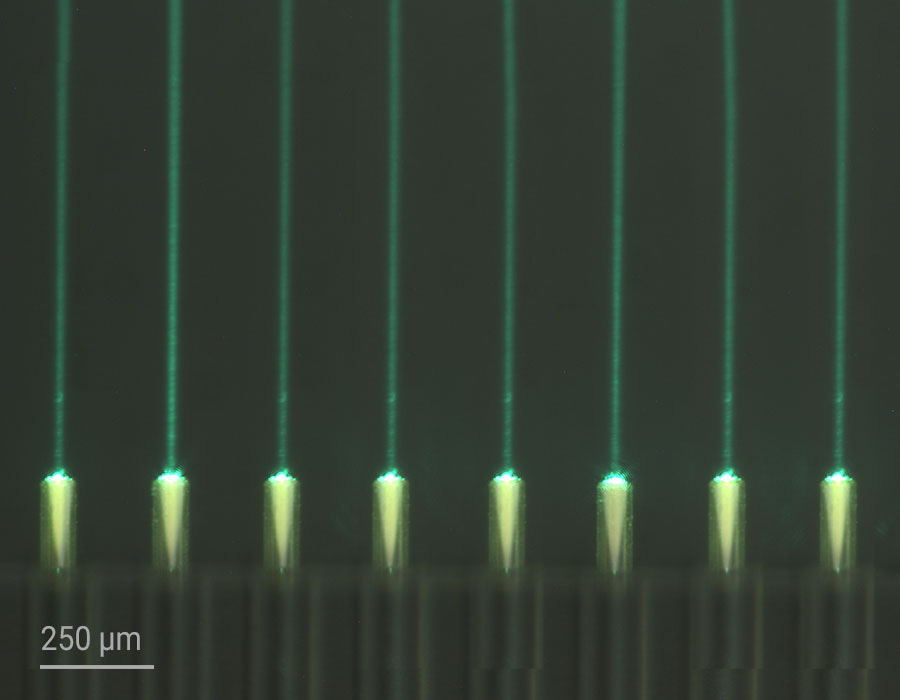
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) have the potential to significantly enhance the computational power of microelectronics while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. However, the production of PIC devices typically involves labor-intensive placement and active alignment of various micro-optical components to create nano-connections. Nanoscribe’s Quantum X align system aimed to solve this challenge.
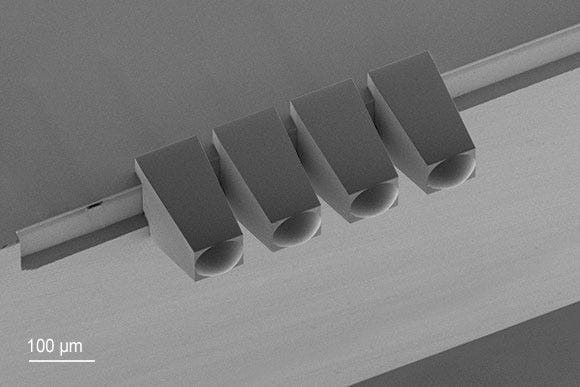
The Quantum X align system automatically detected optical interfaces and spatial orientations of photonic chips and optical fiber cores. This allowed 3D micro-optics of any shape to be printed directly in place. The system even accounted for element tilts, eliminating the need for costly manual alignment procedures. According to Nanoscribe, the system could achieve alignment precision of up to 100 nm across all spatial dimensions.
With a relatively large printing area of 50 x 50 mm, Quantum X align offered versatility in its applications, ranging from microfluidics and sensor systems to miniaturized medical devices, such as those used in minimally invasive endoscopy.
In November 2024, BICO, which had acquired Nanoscribe in 2021, announced its sale for $26 million to LAB14 GmbH, marking another chapter in the company’s evolution.
Source: www.nanoscribe.com





